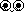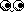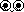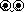
Pupil Deformations
Deformations of the pupil are primarily changes that are
affecting the
inner margin of the iris by paralysis or irritation of the nerves
controlling
the muscles of the iris. Total deformation, in that the natural form
diverges
toward an oval shape, is believed to suggest a disturbance with the
central
nerve association. Partial deformation, or sectoral flattening, is an
indicator
for evaluating the condition of the central nervous system in relation
to organs whose areas are concentrated in the section of the iris
corresponding
to the flattened segment. The ordinary functioning of the nerves to all
areas of the body can be dispersed by misalignments of the vertebrae.
Examination
of pupil tonus can identify problem areas of the spine.
Ventral Diverging Ellipse
Examine for weakness and motor disturbances in lower
extremities with
possible paralysis or pains due to muscle spasms extending from the
buttocks
down.
Right Oblique Ellipse
Observe for right sided paralysis, genito-Urinary
disturbances.
Left Oblique Ellipse
Observe for left-sided paralysis, sexual disturbances, lack of
strength
and energy in the legs.
Unilateral Ellipse
Observe for nervous asthma, bronchus difficulties
Unequal Pupil Diameters
Potential history of diphtheria or meningitis, possible
background of
hereditary syphilitic damage
Horizontal Ellipse
Glandular disturbance with influence upon heart and respiration,
possible
thyroid, depression and motor disturbances.
Verticle Ellipse
Impending cerebral hemorrhage or clotting with possible coma
or paralysis
Frontal Flatness
Tendencies to depression, fatigue, paranoia, melancholy and
guilt feelings,
possible subluxation of C1 vertebra
Inferior Temporal flatness
Observe for weakness in arm and shoulder movement, irritation
and possible
subluxation T1-4, T6 & 7 vertebrae, hepatic insufficiency. Problems
with the movement of both arms and neuralgic pains may be indicated.
The
cause often stems from the cervical plexus. Muscle twitching along the
spinal column can be seen showing nerve impulses being falsely
directed.
Flatting of the right pupil indicates liver and portal vein problems.
Left
pupil flattening indicates paralysis of the heart.
Inferior Nasal Flatness
Observe for irritation to the sacral/lumbar region of the
spine and
associated neural pathways, genito-urinary disturbances, arthritic and
rheumatic signs. Flattening of the right pupil indicates
sexual over excitement leading to impotence. Flattening of the left
pupil,
according to Deck, indicates weakness of the bladder and genitals.
Superior Nasal Flatness
Irritation and possible subluxation to cervical vertebrae,
visual problems,
Digestive and hepatic insufficiencies. Can indicate
spinal
problems that may be secondary symptoms of possible tumor of the thymus
and infectious diseases of the upper cervical cord resulting damage to
the brain stem.
Superior Temporal Flatness
Hearing difficulties - possibly due to dilation of the of the
cerebral
vessels or tumors in the cerebellum, possible subluxation C1-5
vertebrae.
Medial Nasal Flatness
Restriction with breathing with possible heart conditions,
possible
subluxation C1, T1-4 vertebrae. This pupil shape
indicates
breathing difficulties, since the vital lung capacity is much lower
than
normal. These difficulties may manifest as asthma or bronchitis. When
the
flattened area appears in the right pupil only, it indicates hysteria.
When in the left pupil only, shows hypochondriac tendencies. Larger
flattened
areas in the right pupil show spinal vertebrae weakness and disposition
to nervous breakdown. Larger flattened areas in the left pupil show
there
is a disposition to heart problems through faulty nerve impulses.
Lateral Temporal Flatness
Nervous breathing, possible impending circulatory collapse
Typical breathing
problems directly related to the nervous system. Cardiac conditions are
also often present. Coordination of the lungs, chest and intercostal
muscles
are faulty due to nerve regulation and possible lung paralysis.
Ventral Flatness
Weakness in pelvis and lower extremities, poor eliminative
abilities,
possible persistent headaches.
This pupil shape indicates difficulty of movement, stiffness
and weakness
of the legs and feet. It can also relate to spinal misalignments and
may
cause severe headaches.
Frontal Diverging Ellipse
Anxiety states, neuroses, muscle spasms, tendency to cerebral
hemorrhage
and paralysis.